Renal Caluculus
Mrs.Gayathri has been admitted with renal calculi.
a) Write the etiology and clinical manifestations
b) Explain the invasive and non invasive surgical methods of management
c) Explain the post operative nursing management based on three nursing diagnosis
Etiology
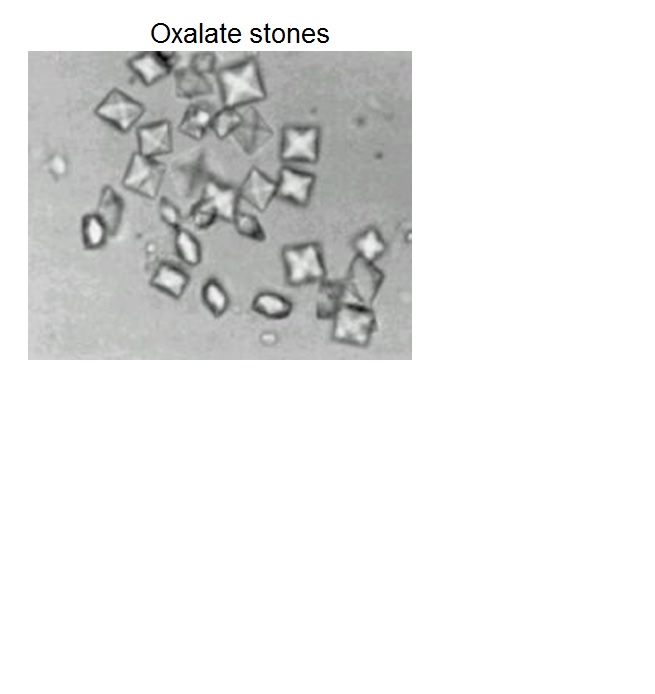
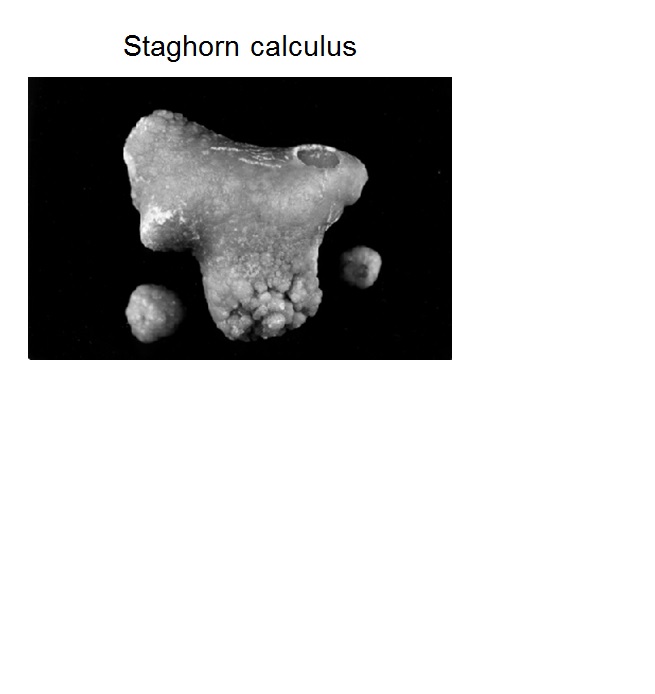
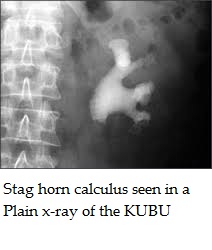
Stone in the kidney
Increased concentration of :
Calcium oxalate
Calcium phosphate
Uric acid
Dependent on the amount of the substance, ionic strength and pH of the urine
Factors favouring the formation of stones :
infection
urinary stasis
periods of immobility
Causes of hypercalcemia :
Hyperparathyroidism
Renal tubular acidosis
Cancers
Granulomatous diseases like sarcoidosis, tuberculosis
Excessive intake of vitamin D
Excessive intake of milk and alkali
Myeloproliferative diseases like leukemia, polycythemia vera, multiple myeloma
75 % of stones calcium based
Clinical Manifestations
Silent stones known
Intense, deep ache in the loin
Hematuria
If infected pyuria, fever, chills
Nausea, vomiting
Diarrhoea and abdominal discomfort due to renointestinal reflexes and the anatomic proximity of the kidneys to the stomach, pancreas and large intestines
Invasive Methods of Management
Nephrolithotomy - open method where kidney is exposed and the stone removed
Percutaneousl Nephrolithotomy - Hollow needle passed into the kidney by USGM guidance - Wire is passed - dilators passe - dilatation done - Nephroscope passed - small stones removed - big stones are fragmented by ultrasound or electrohydraulic probe and then removed
Non invasive Mehtod Management
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy ESWL
The above method may be combined with ESWL
Post operative Nursing Management
Post operative pain - Relieved by medications like tramadol,
Irrigation of the neprostomy catheter or tube as prescribed
Post operative bleeding guarded against. If bleeding occurs appropriate measures
Post operative infection prevented by administration of prescribed antibiotics - cephalosporins
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance Monitoring the B.P. Pulse, Respiration, Electrolyte levels
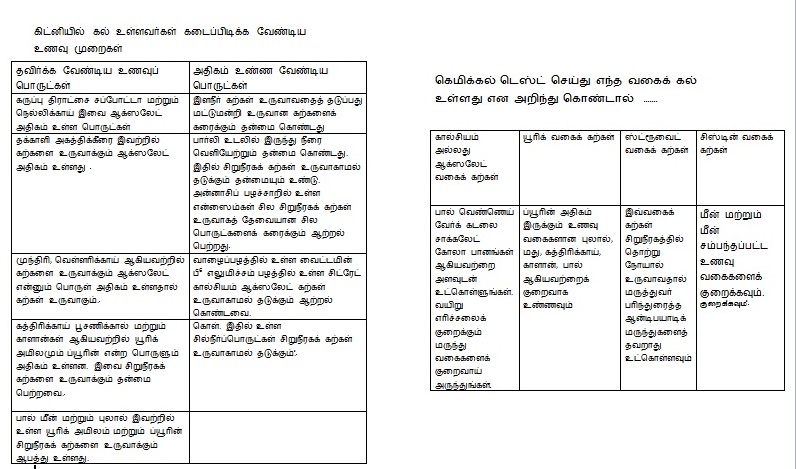
Teach the patient and his family about dietary adjustment and the importance of adequate fluid intake
Give a printed list of items to be avoided in food
Teach them what symptoms need to be reported immediately to the physician - decreased volume of urine, bloody or cloudy urint, fever